In June, the SEO world saw the fallout from the first Google Core Algorithm Update of the year. And from all signs, that update was a big one causing fluctuations all over the place. Some news from Google and the announcement of a whole new search engine from Ahrefs are included in this month’s summary. Let’s jump right in.
May Core Algorithm Update Finished Rolling Out
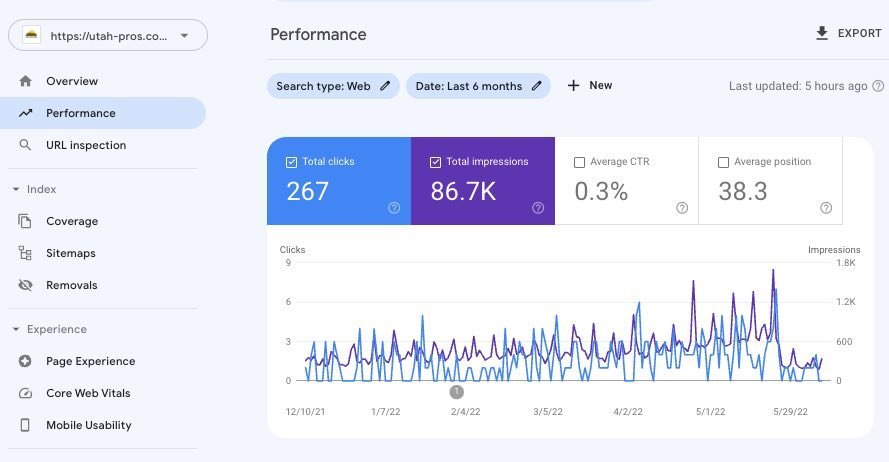
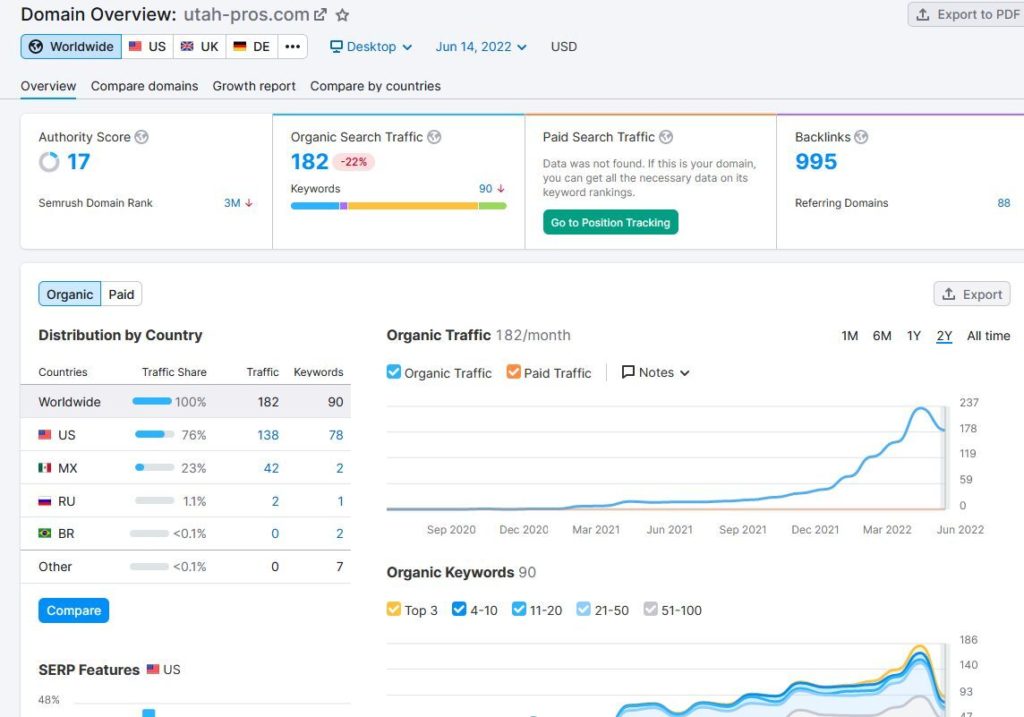
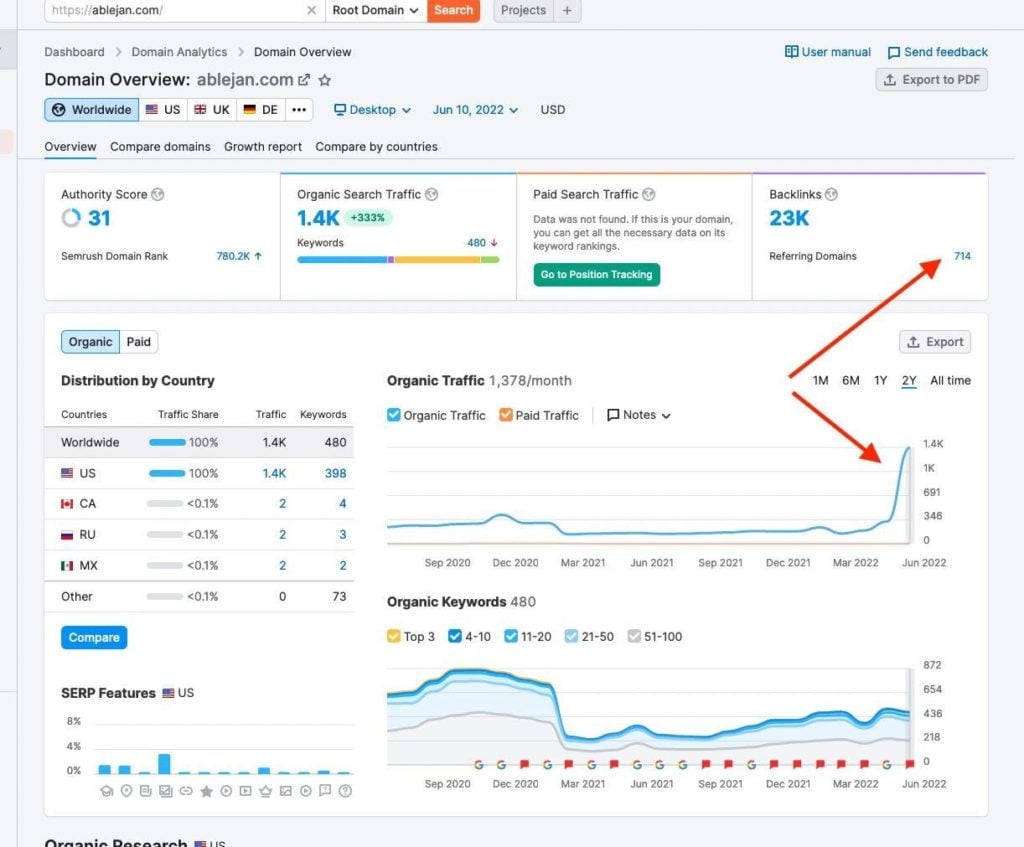
As I mentioned, Google released the May 2022 Broad Core Update, their first big update of the year. SEO’s from across the world noticed fluctuations in rankings. And two of the biggest things impacted by the update include backlinks and long form content. Our analysis shows that websites that only use an on-page linking strategy, or content clustering, dropped positions they held for years for dozens of keywords. Those sites that rose in the rankings all had one major thing in common: MORE BACKLINKS to the domain. Websites that used a mixed approach to linking, meaning both internal and external links, tended to hold their positions. This also includes websites with strong branding that naturally get a lot of backlinks maintained their rankings. So for all those who say “linkbuilding is dead”, this latest update puts that rumor to rest.
The latest Google update also continues to show Google’s emphasis on quality content. More specifically, long form content. Up to when Google released BERT, and subsequently MUM, shorter and more relevant content seemed to rank. But since 2020, long-form content is becoming increasingly important. En masse, long form content is ranking higher and holding the rankings better. With this update, sites that moved up in the rankings had longer, relevant, and detailed content with lots of keywords ranking higher. This doesn’t mean just writing a ton of content that rambles on with no real purpose. But well structured articles and pages that include good keywords, succinct descriptions, and
We also saw the growth of content that also includes video. Take a look at this Tweet. Because more people are consuming video due to the popularity of TikTok and short form video content, user intent is shifting. So it’s looks like Google Algorithm is following suit.
In the video space, there are basically only winners.
TikTok grew a staggering 99%. And Youtube – already one of the most dominant websites in Google`s organic rankings- grew another 23%!😲
In total, video websites gained 25% during this update.
(3/8) pic.twitter.com/TtErApIqTM— Malte Landwehr (@MalteLandwehr) May 30, 2022
Rumored Updates
Beyond the main Core update that rolled out through the first half of June, we saw a few other rumored updates. Around the 19th, there were a lot of fluctuations reported. This is after Google announced the completion of the Core update. But after major updates, it’s fairly typical to see additional tweaks and big fluctuations in the following weeks. One group reported big drops in international traffic around the 19th. Another rumored update is suspected at the end of June around the 28th and 29th. Rank Ranger noted some significant fluctuations around those dates for universal site traffic around the internet.
Only 15MB of Content Crawled?
Some updated documention about Googlebot from the company caused a lot of waves. So much so that Google had to address what was going on. Google originally made an update to their Googlebot help document saying that it only “sees” the first 15 megabytes (MB) when looking at certain file types online. To Google, this isn’t a new process and has been in place for years. But now it’s officially documented. Google says this likely doesn’t mean anything for most website pages, saying there aren’t very many pages on the internet bigger than that. In general, you want to keep your pages as light as possible so it loads more quickly and provides a good experience for both users and the Googlebot. This measurement likely won’t change, but it continues to emphasize what we’ve written for some time that you need to put your most important content, images, or videos at the top of the page to ensure they’re crawled.
Ahrefs Search Engine
Ready for a new competitor in the search space? Ahrefs announced their own search engine. They’ve been a very reliable, industry standard SEO tool for years. And now they want a piece of the search pie. Called Yep, this new search engine will be a general-purpose tool. Ahrefs plans to launch it in all countries and most languages in the coming months. They’re branding it as a Google competitor in terms of capabilities. They say Yep will not collect personal information like your location, name, age, gender and won’t store your search history. Yep will use user keywords, language preferences, and approximate geographic area to improve their algorithm and provide relevant search results. One of the things that makes it stand out the most is their Revenue-sharing model. Ahrefs plans to share 90% of its advertising revenue with content publishers.
“Let’s say that the biggest search engine in the world makes $100B a year. Now, imagine if they gave $90B to content creators and publishers.
Wikipedia would probably earn a few billion dollars a year from its content. They’d be able to stop asking for donations and start paying the people who polish their articles a decent salary.
There would be no more need for paywalls and affiliate links, so publishers who’ve had to resort to chasing traffic with clickbait articles and filling their pages with ads would be able to get back to doing investigative pieces and quality analysis. A citizen journalist uncovering corruption on the side of a full-time job could get compensated without having to spend time trying to monetize content.
And the best thing? You don’t have to be an expert to benefit.
Let’s say that you love pancakes more than anything else in the world. Now you have an incentive to grow that passion – imagine getting fairly paid to share creative recipes, publish photos of your creations and teach the rest of the world how they, too, can make the fluffiest pancakes ever. Independent creators everywhere will finally be able to flourish.”
Ahrefs says their bot/algorithm visits more than 8 billion webpages every 24 hours. They say that’s the second most active crawler on the web behind Google. For now, the results seem to be minimal and a stripped down version of what you’d see on other sites. But that is likely to change as the results become more robust with more indexed web pages.
While it seems that Yep is very robust and built to succeed, we’ll see if people actually start to use it in the coming months.
Duck Duck Go Drops in Popularity
With the launch of one new search engine, we may see the decline of another. Not as a result of Yep, but overall DuckDuckGo has seen a decline in searches. In January 2021, the privacy-centered search engine announced it had over 100 million searches per day, an impressive landmark. But since April of this year, search volume has decreased each month. In March at the start of the war in Ukraine, the founder of DuckDuckGo announced they will start to down-rank sites associated with Russian disinformation. Many users criticized the move saying it violates DuckDuckGo’s commitment to unbiased search. It’s too early to tell if this announcement could have meant a decline in less advertising or perhaps just fewer people using the site. But we’ll watch to see if this decline continues.
Twitter Nofollow Links
In June, Twitter removed the nofollow attribute from its links. This nofollow has been in place since the early days of the site in 2008 and 2009. So essentially profiles, tweets, and other pages on Twitter may now contain followed links. No word on if Google will follow these links, they haven’t commented and likely won’t. But with Twitter’s history of being spammed with links. So there’s no need to start posting a ton of links to your twitter accounts as a part of your SEO strategy. We will keep watching to see where this one goes.
Google Testing New Types of Snippets
Finally this month, we want to talk about new kinds of featured snippets and zero-click search results that Google is testing. In some cases, Google is showing more than one snippet, sometimes up to 4. This is block and list view snippets.
I like these info-cards in mobile results. pic.twitter.com/hGWsAQBN4d
— William Álvarez (@williamalvarez) June 16, 2022
Yep, Google is doing more testing with showing multiple answers within Featured Snippets. We saw it back in April on desktop, now there’s three new variations on mobile. All spotted by @williamalvarez via @rustybrick. Thoughts on this test? More info: https://t.co/j6IUtkB6Zz pic.twitter.com/GufAr00gtr
— Brodie Clark (@brodieseo) June 16, 2022
This means position zero is up for grabs by more websites. This change hasn’t fully rolled out and won’t be available for every query. But it means that there’s more opportunities for these types of results for well-written and succinct content that answers a query well.