This article was first published on March 14, 2015, it was last updated in December 2023.
Of course the goal of any website is to be found by your target audience. Whether you’re providing information or want to sell to your customers, you want to make sure people find your website. You do that with good images, relevant content that include good keywords, authoritative blog posts, and useful information.
All these SEO elements help Google when it crawls your website. You want to make sure all your pages are indexed so that your website can rank. But when Google crawls your website, using its page discovering program called Googlebot, you want to make sure that it understands what it finds on your website. What Googlebot reads determines your page’s relevance and rank.
Then it stores that information. And to really understand what Googlebot sees, you need to look at the Google Cache of your website. This can give you strategic ideas on how to improve your site and where there’s room for improvement. Learn more with our guide and what you need to know about the Google Cache.
What is Google Cache?
Google Cache Viewer is an HTML snapshot of your website. Googlebot takes this snapshot each time the bots crawl your website and stores it as a backup if the current page isn’t available for various reasons. Essentially, looking at the cache search shows what a website looks like the last time Google visited it. Google indexes the site each time it crawls it as well so it can compare with what has changed.
If you’re wondering why your site doesn’t have as much traffic or even how often Google crawls your site, you can find that in the Google Cache site.
The Google Cache is important because the internet constantly changes. Marketing teams and web developers constantly update websites to better improve performance and the user experience.
However, sometimes if a page is deleted or hacked, a user or webmaster might need to access the information that used to be there. That’s when they can go to the cache. The cache can also provide a convenient backup aside from the backups you individually perform.
How to View Cached Pages
There’s a few different ways to view Google cached pages and they’re all pretty easy.
Google Search
Type in “cache”
First is just to add the word “cache” in front of any URL. For example, “cache:https://boostability.com” while using the Google Chrome Browser. Then it pulls up the most recent cached version of the website that looks like this. The box at the top shows some basic information about the cache and how you can access more information.
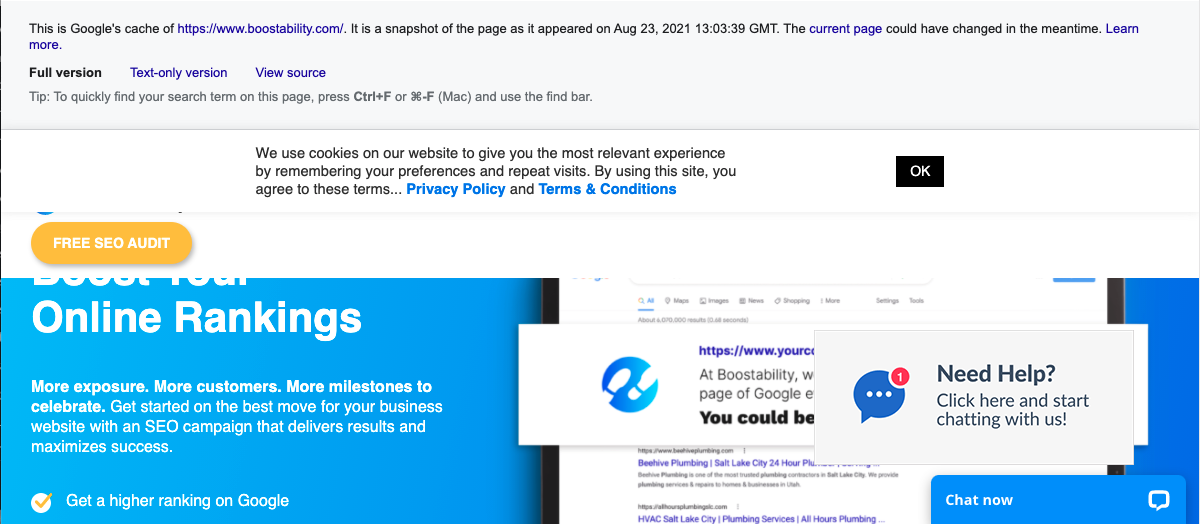
Go into Google’s search bar
The second way to view a cached version of a website is to type in any term or website name into the Google search bar. In this example we’ll use something very simple like penguins. Once you’re given the Google search results, you’ll see a series of titles and meta descriptions that look something like this:
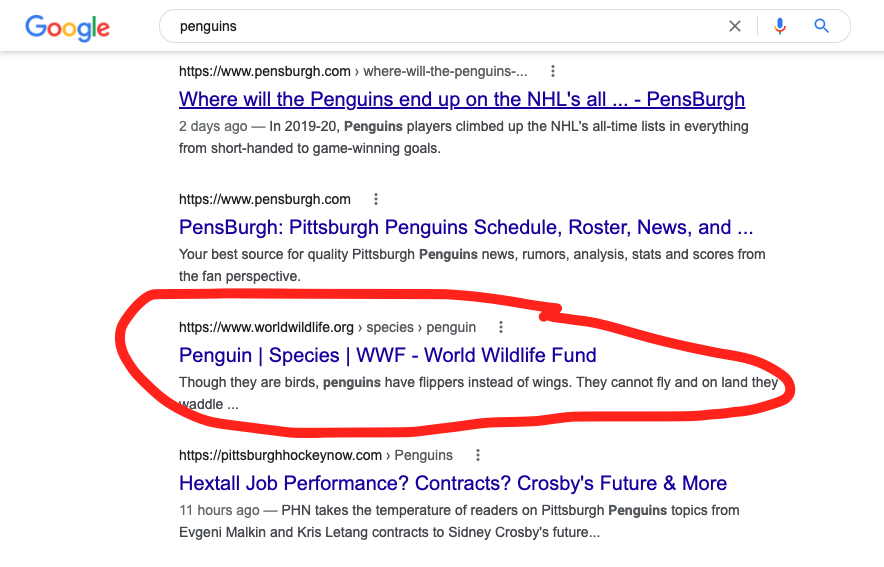
Since I like the third result and want to learn about animal penguins, I’ll go to that website. However, if I want to learn about it’s cache, I’ll click on the three vertical dots to the right of the URL.
That gives you Google’s most recent “About this Result” box that helps results to be more transparent. But at the bottom of that box is the word Cached. That will also take you to the most recently cached version of the website.
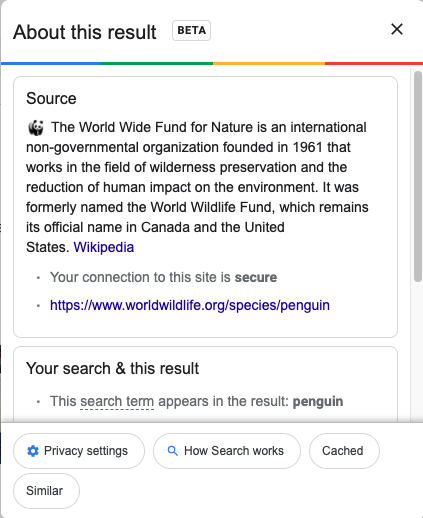
Previously with the “About this result” feature, you would see the URL results with a little green arrow to the right of it. When you click on that arrow, it will take you to the most recent snapshot of the page that Googlebot took.
It could look something like the following:
Google Cache Checker
Google Cache Checker is a tool through Small SEO Tools that lets you enter up to five domains and provide you with a cache URL and a link to let you access the cached version of the page. The biggest benefit of using this tool is that it allows you to do five URLs at once rather than one at a time.
WayBack Machine
Archive.org provides an in-depth visual of a website’s history and also offers a Chrome extension of its Wayback Machine. Using the Google search method or Google Cache Checker only lets you check the most recent versions of web pages.
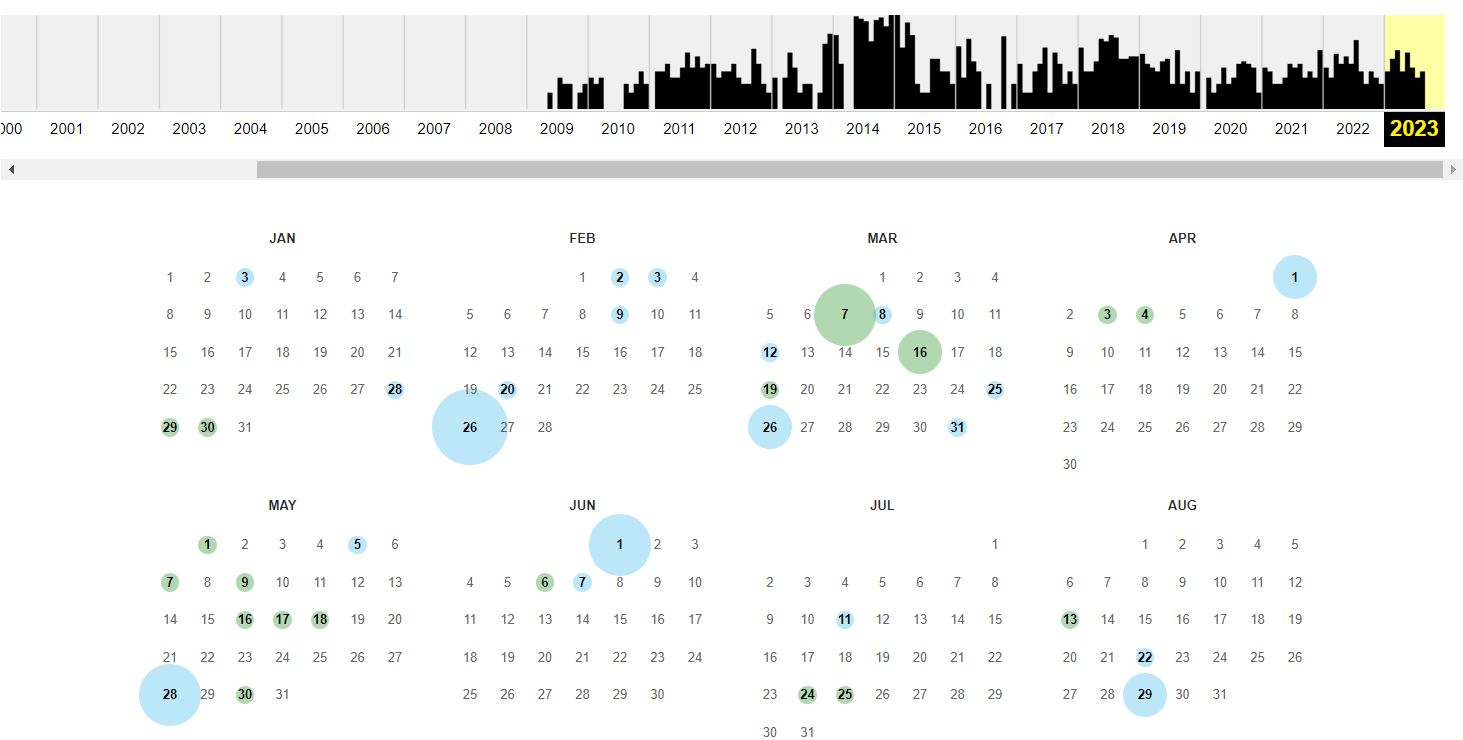
The benefit of using WayBack Machine provides more information as to how many times a website was cached. They break it down day by day and you can click on any date to see what updates had been made.
Why Use Google Cache for Your Website?
Now that we know the HOW of Google Cache viewer, let’s give into the WHY. There’s a few reasons. It can help you out if your page is slow or unresponsive. Then you can check to see where the issues are.
You can see the last time Google crawled your site. And you can see just how Google indexes your website online.
Image & Visual Optimization
When you visit the cached version of your website, you’ll notice a button that says “Text-only version” When you click on that link, you’ll see essentially what the Googlebot sees. The algorithm can’t read pictures—it can only read text.
So when you code your page, you have to make sure you include text elements for Googlebot to read. That’s things like alt text on all your images that use keywords and descriptions to say exactly what the picture shows. Every visual element needs these tags and information-rich content and headings so that Google can understand what’s relevant.
Just make sure that you don’t overload your page with keywords. Googlebot can see them, and if it thinks you’ve stuffed too many keywords onto your page, it will flag your website for unhealthy and unfair SEO practices, which can critically damage your rankings.
How Google Cache Can Show Your Page’s Relevancy
When Googlebot perceives that your website has more relevance and authority, it will index your site more frequently. You can check this frequency using your Google Cache. You’ll find the information in the blue box that appears after you click on the cache link.
If the last cache date occurred today and it updated tomorrow, you would know that your page had high relevance. Google considers your page important enough to update it daily because it can tell your content benefits web readers. It wants to keep that content available even if your website or servers go down, so it saves a copy.
Improve and Enhance Your Content
Google will also crawl and re-cache your page more often if you regularly update your pages with new content. As long as you keep your content’s quality high, the frequency at which you post new content could boost your website’s page rank. But this only works if you have QUALITY content and not just a high QUANTITY of it.
On the other hand, if you find that Google isn’t indexing your website as frequently as you’d like, now you know there’s room for improvement. Start with your content. If you see jumps to your rankings after a new page went live or you wrote a new blog post, start doing that more frequently.
Content is always a good place to start when you want to improve your rankings. And more good content means Google will crawl your website more frequently.
If you’re already posting regularly and Google still doesn’t crawl your website very often, then you need to work on improving your content quality, not quantity. Use more strategic keywords, and improve the E-A-T of your website.
How to Improve Your Website’s Google Cache
Google Cache can teach you many different things about your website. If you looked at the cache date and didn’t feel satisfied with the frequency you saw, take another look at your webpage’s text-only cache and see what you can change about your content. For example, you can:
- Make sure all the text appears in context. If you use a lot of programmed illustrations to convey your meaning, any text you add might not appear in context when Googlebot reads the text-only cache. If every piece of information has textual context, Googlebot can read all your content and determine its quality in addition to its relevance.
- As mentioned, content plays a big role here. You should assess it in a stylistic and technical sense. It should have correct spelling and grammar, but it should also say something useful. It shouldn’t include obvious statements, nor should it rehash information that you can find on any website. Make it sound unique, informative, and professional.
- Adjust the page’s keyword density. Integrate your keywords so they sound natural in your content. Don’t use too many keywords or too few. For example, if your content includes 300 words overall, it shouldn’t include 10 keywords. Nor should it include only one. Find a balance so Google doesn’t penalize you either way.
Does Google Cache Have Limitations?
While Google Cache is a wonderful tool that can help you in your SEO strategy, it does have some limitations. It gives you a snapshot of what Google sees as it crawls your website. But Google will never reveal exactly how its algorithm works. So the cache can give you many ideas, but it’s not perfect.
The cache also might not get updated every time it crawls your website. It can tell you when it crawled the site, but the snapshot or the text only older version might not update every single time, especially if it crawls your website more frequently.
Google also doesn’t Cache every single website page. It will index every page, but not all are stored in the cache. So you can’t rely on it for a backup.
Sometimes if your website is powered by JavaScript too, the cache will appear empty. Unless the source code specifically rends the content in a way that Google can read it, you will see an empty cache.
Again, that doesn’t mean it’s not indexed. So don’t stress if your website has JavaScript. It’s one of the most popular languages in the world for a reason.
If you need some help optimizing your website with white label SEO services, contact us here at Boostability and we can help you get started. Get in contact today to learn more!


