Top 10 Ranking Factors For Link Building

Most experts will agree that backlinks have the greatest off-site impact on the ranking of a website in search engines. Do a quick search online and there are hundreds of off-site factors that will supposedly make your rankings climb.
Google hasn’t officially stated all factors that affect rankings, or which are merely myths created by marketers.
I have been growing websites for years, and have been involved in online marketing for as long as I can remember, so I like to think I know my stuff when it comes to on-site and off-site SEO.
So here they are, 10 link-building ranking factors that do make a positive difference to your website rankings based on my own experience and the studies of others.
1. Number of links from root domains
A root domain is a website’s core address. For example, the root domain of Boostability is www. Boostability.com.
A website that has 75 links from root domains will rank higher than a website with only 40 links from root domains, assuming everything else is equal.
Moz found that websites ranking in the top 8 search positions typically had between 100-200 root domain backlinks, with those websites ranking 1st and 2nd being closer to 800:
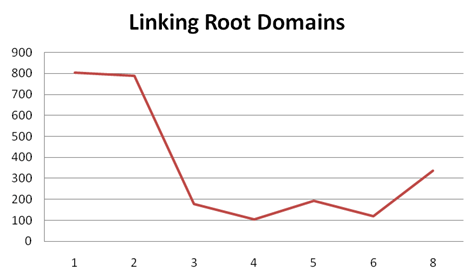
(Source)
2. Domain age of linking website
The longer a website has been on the Internet, the more trusted it is by Google. Spam and thin content sites are typically dumped 1-2 years after creation, whereas legitimate website owners continue to renew their domain lease.
Some marketers believe that Google has a Sandbox algorithm that stops newly created websites from ranking to their full potential during birth to stop them from ruining their search engine results, thereby further cementing the importance of domain age in link building.
The older a website is, the more weight the backlink carries, which was proved in a test carried out by SEO Hacker.
3. Links from Separate Class-C IPs
Once website owners realized that more backlinks from root domains resulted in boosted rankings, many started creating dozens of new websites that linked back to their main site and outsmarted Google…. for a brief period.
Google then changed their algorithm to give higher weight to backlinks pointing to your website from separate Class-C IP addresses.
What this effectively means is, if you host several sites on a single server, all your sites will belong to the same Class-C IP address, and linking one site to the next won’t count for much.
4. Anchor text
Anchor text is clickable text tied to a hyperlink. In other words, when you’re reading through a web page or a blog post, for example, the anchor text is the little underlined (and usually blue) text that you can click on to visit another web page. Often anchor text will be words like “click here” or “read more.”
Google states, “Anchors often provide more accurate descriptions of web pages than the pages themselves.” Based on that, anchor text is incredibly important as it lends itself to the Google algorithm by indicating “these words mean something to this link.” That means that Google takes into consideration what words are actually highlighted and linked. The more often those words are linked to your page from unique sources, the more likely the words are to be a highly ranked keyword for your business.
Your anchor text is a good opportunity to use long-tail keywords (keywords that are three or more words, such as “awesome cake in Chicago”). Choose your anchor text wisely and try to choose three words that best describe what you are linking to. This will benefit your keyword strategy in addition to increasing the click through rate of your links, just a side perk of optimizing your anchor text.
While having dozens of links using the same anchor text sounds like more points toward your keyword optimization, it would be considered keyword stuffing if too many areas of your website used the same internal anchor links or if any other third-party website overused one anchor text. This can act as a web spam signal to Google, and a sign that you’re trying to manipulate their rankings.
As a rule of thumb, your external backlink profile should not have more than 10% of keyword anchor links.
5. Backlinks from country domains
The country top level domain (TLD) of where your backlinks come from plays an important role in ranking your site geographically.
If your business only caters to the United States, but your backlinks are coming from India, China, Thailand, and Brazil, that won’t improve your website’s ranking in the US.
However, if your links are from .com domains or com/us pages, this will jump your site higher in nationwide searches and increase its legitimate appearance.
6. Domain Authority (DA) and Page Authority (PA)
Google’s biggest challenge is to ensure low quality sites don’t rank higher than high quality sites.
DA and PA is a Moz-specific number that they put out that represents the trustworthiness of a domain, and each page within a domain, based on the number of quality links pointing towards them.
For example, if a website has 900 backlinks which are from low quality sites, it will have a lower DA and PA than a website with 200 links that come from high quality sites.
You can find your website’s DA and PA using Moz Open Site Explorer:
Sites with a DA and PA above 40 show an immediate sign of quality. If the bulk of your backlinks come from lower quality websites, with a DA and PA of 14 or less, this can negatively impact your website if done in bulk.
7. Paid links
Paying for backlinks is against Google’s Terms of Service and, if caught, can cause your website to be de-listed from Google. If you’re paying for link placements, ensure your URLs are no-follow, as these do not pass Page Rank and will not impact your website negatively. You do have to take into account your overall backlink profile as a wide variety of types of links helps your authority.
Google is not shy to penalize websites that pay for backlinks because doing so reduces the integrity of their search engine.
8. Link diversity
Having the majority of your backlinks coming from a single source (social media or web forums) is often considered a web spam single.
Links should come from an array of sources such as:
- Blogs
- News outlets
- Websites
- Forums
- Blog comments
- Social media
- User profiles
Give your website more credibility and trust by increasing the weight of each backlink. A diversified backlink profile is important.
9. Linking domain relevancy
To stop website owners from buying backlinks from any site with a high DA and PA, backlinks that come from relevant niches are given a higher preference.
For example, if Boostability was linked on a marketing website, in Google’s eyes the backlink is weighted higher than if we were linked in a car or fashion outlet.
After all, why would a marketing website be mentioned on a car site or fashion blog?
Something sounds fishy.
Backlinks within relevant niches count for a lot.
10. Link sentiment
Google looks for keywords to see if links that mention your business are written in a positive or negative sentiment – for example, if someone is reviewing your business but has had a negative experience and linked your site in the review this will decrease the value of the backlink.
The better the sentiment, the more value Google will attach to the backlink.
Summary
There are several more factors that impact the weight of a backlink pointing to your website, but I believe if you focus on the 10 factors above when building white-hat links, you will see a huge difference in where your website ranks.
How many of these link building factors do you take into account when building your site’s backlink profile?
