How Do Search Engines Work and Why Should You Care?

This article was first published July 20th, 2021, and was last updated July 2023.
How do search engines work? The way they work may be a mystery for some. However, if you take a closer look, you’ll find that there’s no mystery, only some basic rules.
68% of online user journeys start with a search engine. Understanding and following the inner workings of search engine optimization (SEO) can help you boost your website’s rankings and be seen by more people.
Follow along this quick guide to learn how search engines work—from crawling and indexing to the ranking of pages. You will find out how to rank your page on the top and what makes a search engine-friendly marketing tactic.
Let’s go!
Table of Contents
Why Should You Care About Search Engines?
How Do Search Engines Build Their Index?
- URLS
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Ranking
- Backlinks
- Link Authority and Relevance
- Topical Authority
- Expertise
- Experience
- Authoritativeness
- Trustworthiness
- Page Speed and Mobile Friendliness
How Search Engines Deliver Personalized Results
- Location
- Language
- Search History
What are Search Engines?
Search engines are online tools that help find relevant results to your search queries. Examples of popular search engines include Google, Bing, Yahoo, DuckDuckGo, or Yandex. Most of them work the same way, yet, you’ll find some stark search differences if you compare the top three.
Search engines have evolved in the past decade or two. They now understand queries better and provide higher quality search results, too. You can search by just typing in one word, multiple words, or even sentences and questions.
There are two types of search results on the web:
- Organic results
- Paid results
Organic results show all the pages that are relevant to the user’s search. Appearing in organic results is free. You cannot pay to be featured. If you’re looking to pay for a spot, paid search is the way to go.
To get into one of the paid spots, simply register an account on Google Ads or Bing Ads to get started. You don’t need to be a digital marketing expert to launch a few ads, either. Google Ads, for example, is a beginner-friendly interface where you can set your own budget and submit as few or as many ads as you like. Search engines make most of their money through ad dollars.
Why Should You Care About Search Engines?
As a business owner, why should you learn how search engines work? The reason is because this is the first step to understanding SEO. Even if you outsource this part of your marketing, it’s good to stay in the know.
Ranking in the top 10 rankings of Google has never been more important than now. Studies show that 67.50% of all clicks on a Google search page go to the first five organic results. So the higher you can rank your pages, the more visitors you will attract.
The best part of SEO is that it’s not just about the traffic. The conversion rate of organic visitors is one of the highest in digital marketing. After investing in search optimization, your business could break even in as little as five months, according to statistics. This is why more and more B2B companies integrate SEO into their content strategy.
Business owners now understand that SEO is not about trying to “game search engines with gimmicks.” It’s about creating relevant content and then helping the algorithm find it.
How Do Search Engines Build Their Index?
When you enter a search query, you may get your results in just a matter of a few seconds. This wouldn’t be possible if you were searching the web itself. Why? Search quality expert Matt Cutts explains it best:
“When you do a Google search, you’re not actually searching the web. You are searching Google’s index of the web. Or at least as much as we can find.”
How does the index get put together? How can you get on top of the search results fast? Keep on reading to find out how search engine crawling, indexing, and ranking work.
1. URLs
To build the index, a search engine needs to continuously find URLs. How? The process is simple: web crawlers find and detect and identify new links (also called backlinks) on already indexed web pages and follow them to new pages.
You can help your new pages get discovered via sitemaps or individual URL submissions to Google Search Console (formerly known as Webmaster Tools). But keep in mind that these tactics won’t help you speed up your site’s discovery. Sitemaps, for example, are part of a standard SEO setup. Their purpose is to help search engines find, locate, and understand your web pages easier, not to get discovered faster.
2. Crawling
Search engine crawlers that scout the web are also called spiders. Spiders are automated scripts whose task is to visit and download new pages on the web. There’s just one caveat: they do not crawl them in the order of discovery. The crawl queue (also called crawl budget or crawl rate) happens based on one of the following factors:
- The URL’s PageRank
- How often the URL changes
- How new the page is
You can review your crawl rate in Google Search Console. However, as Google itself states on their help page, it’s not something smaller sites need to worry about. Here’s what you need to know:
“If a site has fewer than a few thousand URLs, most of the time it will be crawled efficiently. Prioritizing what to crawl, when, and how much resources the server hosting the site can allocate to crawling is more important for bigger sites or those that auto-generate pages based on URL parameters.”
3. Indexing
Once spiders have processed all the web page data, they get into the index. Getting your website indexed by major search engines like Google and Bing is the last step before you can appear for users. This step is called ranking.
4. Ranking
Once crawling and indexing are out of the way, it’s up to the search engines to decide which websites and pages get to rank in which order. This process happens through search engine algorithms.
These algorithms test the indexed pages against multiple factors to determine their usefulness to the user. Google wants users to have a seamless experience, so these factors could include content quality, relevancy, backlinks, topic authority, and hundreds more. The better the page fits the user’s query, the higher it will rank.
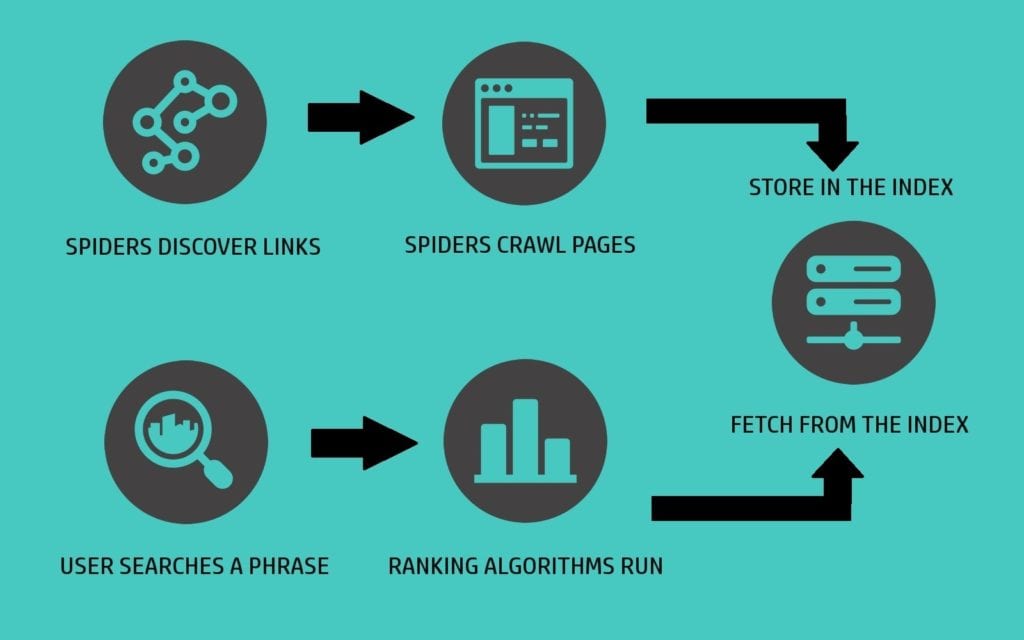
The below flowchart shows how the whole process comes together: from crawling and indexing to the search results page. Some tasks run simultaneously to deliver immediate results.
How Search Engines Rank Pages
What gets on search engine results pages (especially on page 1) involves 200+ processes. These processes run through the index in just a few milliseconds for each user and each search query. In the following sections, you’ll learn more about some of the most important ranking factors and how you can build your strategies around them. As Google’s search engine has the biggest market share in most countries, all of the examples will be taken from Google’s processes.
1. Backlinks
The two main ranking factors on Google are content and backlinks. When a page links to another page, it’s a vote of confidence in Google’s eyes.
Both the quality and quantity are taken into consideration for the formula. Gone are the days when you could just buy up links and hope for the best. Today, you need to earn your links organically.
Gaining backlinks is a long game in any SEO strategy. First,you need to create a lot of high-quality content, then share them across the internet. Eventually, your site will be noticed and other websites will start linking to you.
2. Link Authority and Relevance
Not every link is created equal. The better links you get, the more you can improve your ranking. But what is a “better link”? Think about getting a link from a 2-week-old blog vs. an influencer’s content-rich website in your niche. The difference is in the authority.
Link authority is a factor that establishes the power of backlinks from any given website. The more authoritative the backlink’s website is, the more pull you’ll get in your rankings.
Aim to gain relevant links from big names in your industry. For example, if you have an ecommerce store selling chocolate, then get a backlink from a prominent chocolate blogger. Most SEO tools have a way of measuring a website’s link authority, too. Refer to your tool next time you’re doing your SEO audit or research.
3. Topical Authority
Being strategic and authentic in your content marketing is a must for good SEO. You can no longer just spin some content and jump to the first spot on Google. If you regularly accept blog content from new writers, it’s a good idea to run a plagiarism check on their work before hitting publish. This is a common practice that protects site owners and covers at least one aspect of quality content.
The more content you create about a certain topic, the more rapidly you will increase your authority in that niche. You can follow Google’s E-E-A-T formula to gain momentum in your niche. The acronym stands for Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
Pro-tip: You can also pick up specific SEO practices in line with the platform you are using to promote your blog. For example, while building your blog, you can hire a web developer that can boost your WordPress SEO efforts by integrating certain plug-ins to promote your content more effectively.
Expertise
Showcase your knowledge by adding pages with high-quality content. “Quality content” is the staple of any SEO strategy. It includes well-written, well-researched, and highly informative content for the audience. For example, if you run a coconut oil store, having articles about coconut oil uses on hair would be considered useful, quality content.
Experience
In December 2022, Google added an extra E to the acronym E-A-T to form the new and improved E-E-A-T. The extra letter was added to focus on the aspect of Experience. Do writers have real, first-hand, or real-life experience using what they write about? This is where this element comes into play.
Authoritativeness
Ensure to have any industry badges, or other achievements displayed to show your authority on the topic. You can also do some social listening to understand where you stand against your competitors. Social listening in SEO includes monitoring keywords in your niche and keeping an eye out for link-building opportunities.
Trustworthiness
Regularly refreshing your content is one of the ways you can increase SEO traffic and boost your site’s trustworthiness.
4. Page Speed and Mobile-Friendliness
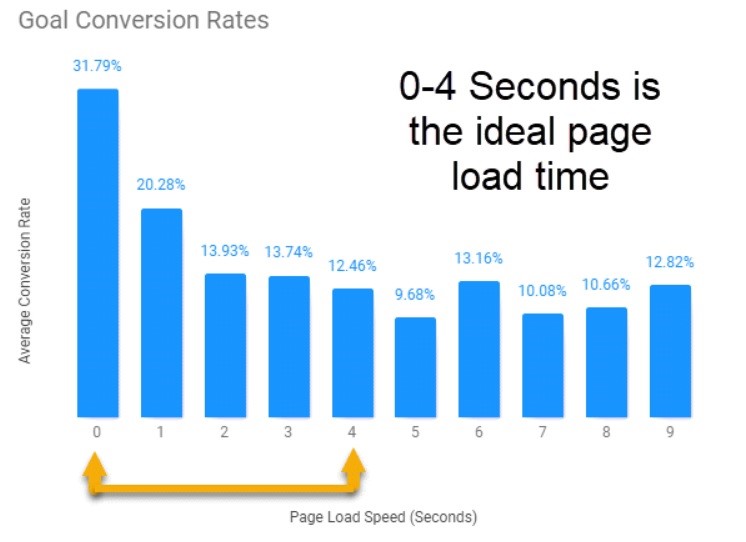
People have low patience for page load times these days. They expect websites to load in just seconds. Around 70% of consumers admit that page speed impacts their willingness to buy from an online retailer.
With that said, your site does not need to be the fastest to rank. As long as it’s within a good range of 0 and 4 seconds, you’re good to go.
Check your website’s speed in Google’s PageSpeed Insights to get an idea of your numbers.
Another key factor in your website’s ranking is how you look on mobile. As more and more people use smartphones to search, Google is also placing higher importance on it. In 2018, they made it official by announcing a “mobile-first” ranking. This means that Google now prioritizes its rankings based on your site’s mobile performance.
Check your website’s mobile-friendliness with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to see where you can improve.
How Search Engines Deliver Personalized Results
Your search results for the query “sushi restaurants” will not be the same if you’re in New York vs. if you’re in Tokyo. It’s not just because of the location, although that’s a significant factor in this case. Let’s review what factors can alter your search results page.
Location
Google uses your location to determine what type of content to show you. The search engine can see your whereabouts by your account’s location settings.
Your location impacts the search results page beyond the map pack. For example, when searching for products or services, you will find that Google serves up mostly local businesses.
If you have a location-relevant business (such as a brick-and-mortar store), then it’s a good idea to take advantage of some local SEO tactics. Register on Google My Business, create localized landing pages, or hone in on local keywords.
Language
For the best user experience, Google is always trying to show the most relevant language. The search engine can detect the language by the user’s browser settings and again, by the location settings.
For some users, it won’t be as clear-cut, though. In these cases, Google expects webmasters and SEO professionals to have a proper hreflang set up on their websites.
Search History
One near-perfect way search engines personalize search results is by looking at a user’s query history. By evaluating the type of content that a given user has searched for, Google can successfully determine which results to show next time around.
This is not something you can specifically optimize for, rather a nice perk of Google delivering the right users to you.
You’re Ready to Rank Your Pages Now
Congrats! The way search engines work is no longer a mystery for you. Now you know how crawling, indexing and ranking happen. You also know that quality content, authority, links, and trustworthiness are one of the many factors to rank high.
You can immediately get started by:
- Adding quality content to your site and updating your content frequently.
- Keeping your content index-ready by following the rules of E-E-A-T.
- Optimizing your site for local searches and mobile devices.
SEO and ranking factors are not going away anytime soon. Ensure you keep your business relevant by optimizing your site for humans and search engines alike. Let Boostability, the #1 white label SEO provider help you out! Learn more about our SEO services today!