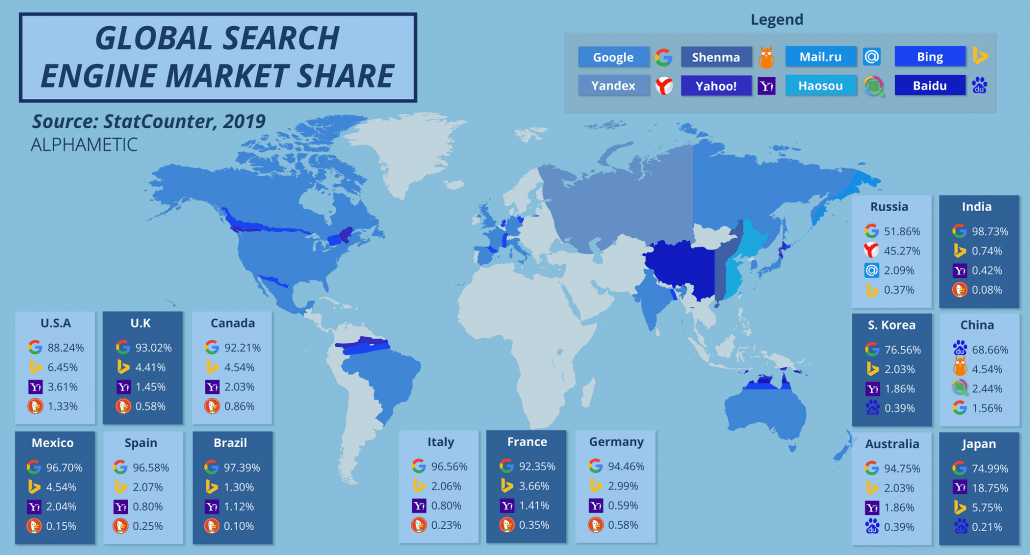
This article was first published on July 29th, 2021, and was last updated February 2023.
Google is the biggest search engine in the world for a reason. It makes a move, and most other engines follow suit. But we all remember the early days of the internet. With AskJeeves, Alta Vista, Infoseek, and so many other now-defunct search engines once helped us find what we were looking for online.
So what happened? Why did Google rise while so many fell? And does that mean that Google is the only option when you want to search for something online?
There are still dozens of different types of search engines out there. There are more popular search engines like Bing, Yandex, and others that focus on privacy that are emerging on the big stage. And what is good SEO for Google optimization, is good for all search engines in existence. And which one you use is entirely up to you!
This article will walk you through the other types of search engines currently in existence, why you would use them, and some of their best features.
Table of Contents
Aside From Google, What are the Different Types of Search Engines?
- Crawler Based Search Engines
- Google, Bing, and Yahoo
- Yandex
- Baidu
- Openverse
- AOL
- Excite
- Privacy Based Search Engines
- DuckDuckGo
- Swisscows
- Startpage
- Search Encrypt
- Gibiru
- OneSearch
- Crowd-Sourced Based Search Engines
- Wiki.com
- Boardreader
- Social Change Search Engines
- Ecosia
- giveWater
- Ekoru
What is the Difference Between a Web Browser and Search Engines?
What are the Commonly Used Web Browsers?
- Chrome
- Safari
- Brave
- FireFox
- Opera
- Internet Explorer
- Microsoft Edge
How Can I Tell Which Search Engine I’m Using?
Aside From Google, What are the Different Types of Search Engines?
Crawler Based Search Engines
Google, Bing, and Yahoo

At least in the western world, there are three main types of search engines that get over 95% of search traffic. These are Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
Google is a major search engine and gets a majority of that traffic. But many also prefer Bing because it has more of a visual interface. Yahoo has waned in popularity in recent years, but that doesn’t mean it’s obsolete. These are key search engines that can help you find basically whatever you need online.
Google focuses mostly on simplicity with its interface not offering any extras besides the search. Bing offers current news, trivia, and fun background photos. Yahoo provides a lot of information right from the home page. And the search engine itself is actually powered by the Bing algorithm.
We’ve written in–depth about the differences between Google, Bing, and Yahoo previously. So if you want to learn more about those three and why you might want to use them, read our guide. The rest of our article will go into other types of search engines other than these three.
Yandex

Yandex is one of the biggest search engines in the world. But for users outside the United States. Yandex mostly serves searchers in Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Turkey, Ukraine, and other areas of eastern Europe. Google is still used in some of these countries, but Yandex is more popular, and SEOs optimize for this algorithm rather than Google.
Yandex stands for “Yet another indexer”, and is actually the 5th largest search engine in the world. From its own website, Yandex “uses a search index, which is basically a database of all the words and their locations known to the search engine.
A word’s location is a combination of its position on a web page and the web page’s address on the internet… A search index registers every word the search engine has ever come across. And unlike a phone book, which lists names and addresses, a search engine has more than one “registered address” for each word.
Yandex has two crawler-based search engines, one that indexes all the web pages it comes across, and one called Orange that does express indexing to make sure the most recent documents or web pages are available. Both crawlers have a so-called waiting list of pages to index. And websites can add to that list by using the Yandex Webmaster service.
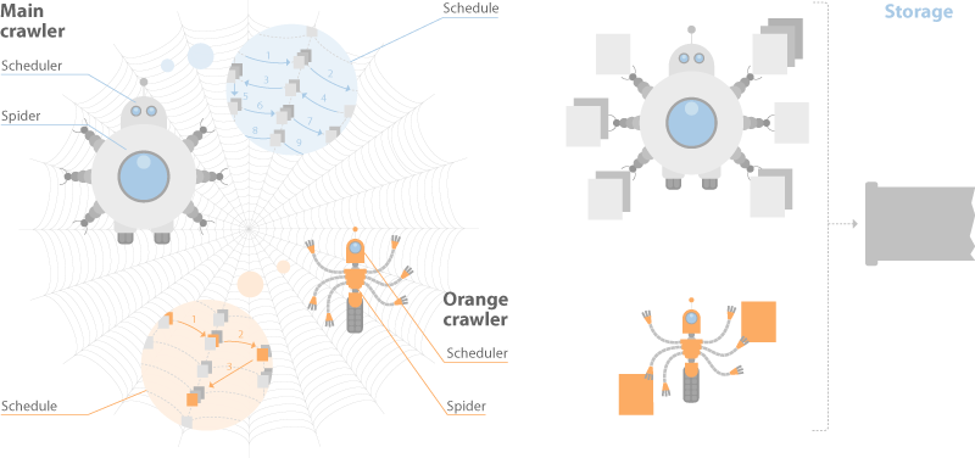
The Yandex search engine has two main stages. The first step crawls the web and indexes them. The second then searches the index to answer a specific user query found in the database.
Baidu

Similar to Yandex, Baidu is a top search engine in the world and is the most popular in China. Well over 70% of China’s population uses Baidu as its primary search engine. Baidu is very similar to Google in that it offers a lot of different search products like paid search, mobile, translation, games, music, and much more.
Baidu is a Chinese company that operates under Chinese government laws, regulations, and even censorship of certain content. But because it’s a company that is already part of the culture, its search engine that focuses on the Chinese language and culture means it can better serve the Chinese market from massive cities like Shanghai and Beijing to small rural towns.
This helps its dominance and why Google has struggled to gain a bigger footing in China. Baidu also works outside of China, just like Google works inside China. But it’s primarily created exclusively for users in China and will return results in Chinese, no matter what language you enter.
Baidu has two primary segments, Baidu Core, which involves keyword-based marketing and AI, and iQIYI which offers online advertising.
Openverse
Openverse, previously known as CC Search which stands for Creative Commons, is a “Tool that allows openly licensed and public domain works to be discovered and used by everyone.” Essentially, it’s a visual search platform that allows you to search for any public domain images, though they have plans to expand to things like audio and video. More than 300 million images exist on Openverse.
One of the key differences is that all code for Openverse is open source, and they welcome community contribution. This is a good platform for visual elements if you need them and don’t want to pay for something like Adobe Creative Cloud or iStock, but still want to search for various images.
AOL

AOL, formerly known as America Online, is both a search engine and an online media company. Starting out as a software company back in 1985, they are considered one of the early pioneers of the internet and eventually one of the biggest search engines online. Currently they hold 0.06% of the world’s search engine market share.
On June 23rd, 2015, AOL was acquired by Verizon Communications for $4.4 billion. They provide advertising services such as AOL Advertising, AOL mail, and AOL Platform.
The user experience of this website includes features such as the search bar, national news articles, local news, and weather updates.
Excite
Excite is one of the oldest search engines still in existence. Though it’s not nearly what it used to be. Excite first showed up in 1995 and piloted the “crawler” technology to look at websites and return relevant search results.
Like Yahoo, Excite is considered a “portal” that does indeed offer search results, but also a bunch of other services like email, news, weather, games, and more. Excite was purchased by Ask in 2004 and still exists to offer services in the U.S., U.K., Germany, France, Spain, Italy, the Netherlands, and Austria.
In the U.S., search results come through a metasearch tool that combines PPC and organic search tools like Google and Yahoo. In the UK and other parts of Europe, Excite just takes the results from Ask.
Privacy Based Search Engines
DuckDuckGo

The conversation around online privacy is growing. People want to make sure their information is secure online. And big tech has sometimes been painted as the enemy of privacy.
Enter DuckDuckGo. It’s a private search engine that prides itself on helping you stay anonymous online. Most websites will track cookies to better serve your ads or more personalized search results. Whereas DuckDuckGo keeps your information private without those tracking cookies.
So many ask then, how does it make money? It still serves ads but is not personalized in the way you might see on other websites. The ads show up depending on your search results page, not your search history.
You can see the appeal of a search engine like this. Many like being able to “stay off the grid” so to speak. This engine is also rapidly growing in popularity as people like to keep their information and search habits private. Does that mean you need to have an SEO strategy around DuckDuckGo? Read our guide here.
Swisscows

Swisscows also brands itself as a more private search experience, along with the philanthropic option to give back as you search. It launched in 2014 in Switzerland but serves many languages. Swisscows doesn’t track or collect data. On their website, they even say they have their own servers and don’t work on the cloud, and hold their data center in the “Swiss Alps – THIS is the safest bunker in Europe!”
Swisscows also brands itself as a family-friendly search engine that does not list any pornographic or violent content. And it forwards donations from the paid search ads to needy children around the world to provide food, shelter, and educational access in places that wouldn’t otherwise.
Startpage

Startpage is a Dutch search engine that gives users the option to search anonymously. Startpage prides itself on being smaller than Google or Bing and more private. They make a point of not tracking your activity online.
It’s similar to DuckDuckGo and its privacy controls. They don’t collect or sell search history, they don’t allow 3rd party ad trackers or cookies, and you can search anonymously to avoid online profiling and targeted ads.
Once you click on a website, those controls are gone. You can also add Startpage to Chrome as a default search engine option. Even though Startpage is a Dutch company, you can search in a variety of languages.
Search Encrypt

Many people, especially in the European area, have a big focus on digital privacy. That’s why there are a growing number of privacy-focused search engines. We’ve already talked about a couple.
However, one more popular site is Search Encrypt. Like the others, they don’t track your search history and don’t create profiles around users. Search Encrypt’s MO is to encourage safe browsing practices online.
Search Encrypt is a Google Chrome or Firefox extension so you can learn better privacy habits online. It will tell you when your search is redirected. And it makes Search Encrypt your primary browser, though you can turn it off and search with Google or Bing.
Gibiru

Yet another privacy-focused search engine is Gibiru. It calls itself a private and uncensored search engine. When you search, you get both “all results” and “uncensored” options. Meaning that you get completely algorithm-based search results and nothing that could get filtered based on possibly dangerous or incorrect information.
Gibiru also provides HTTPS 256-bit encryption to ensure total secrecy. Gibiru doesn’t track IP addresses, place cookies, or sell data to advertisers to retarget ads.
Gibiru also provides a mobile app called Wormhole that allows anonymous mobile web search engine surfing. It’s like its own search browser that’s just an app.
OneSearch

OneSearch is a Verizon search engine that launched to be a DuckDuckGo competitor. Verizon is trying to capitalize on that emphasis and focus on keeping user data private. The search engine itself is powered by Bing search results, with paid ads coming from Microsoft Advertising (formerly BingAds).
But the difference in browsing with OneSearch is that it doesn’t deploy tracking cookies for retargeting. It encrypts search keywords and builds results based on those keywords. Then the encryption key expires after one hour, stopping third parties from tracking a user over a period of time. OneSearch will appear on Google’s search choice screen for Android device users in the EU starting this year, which may help it grow in popularity.
Crowd-Sourced Based Search Engines
Wiki.com

This is a wiki search engine created by independent developers as a way to search all Wikia wikis, Wikimedia, and other Wiki websites. But it’s powered by a Google Custom Search. It’s a good way to search online encyclopedias to learn more about a certain topic. But recognize that it’s crowdsourced information and might not always be fully correct.
Boardreader

Boardreader is a search engine based around “connecting communities through search”. Boardreader is a great resource if you’re interested in finding, viewing, and analyzing information from different discussion boards about a specific subject. It pulls from different social media sources, Google Groups, Epinions, and more.
Social Impact Search Engines
Ecosia

Ecosia is the search engine that gives back to the environment. This is a fairly new player in the search field. It’s been around for a while but is really growing in features and popularity in recent years.
What sets Ecosia apart is that you get to “plant trees as you search!” In other words, a good fraction of the profit made from the search engine goes back to planting trees all over the world. So the search ads on Ecosia bring in money, which then goes back to a great cause.
Ecosia is growing in popularity in its short time on the internet. It has 15 million active users with approximately 130 million trees donated and planted. Ecosia is even one of Google Chrome’s default search engine options! So if you’re looking for a more eco-friendly way to search, check out Ecosia.
giveWater

Just like Ecosia, giveWater is a social change search engine that looks to help provide clean water and effective sanitation. When you use giveWater as a search engine, paid search ads generate income for giveWater.
GiveWater distributes a portion of our profits from those ads to their charitable partners. From there, those partners use the donated funds to provide clean water and sanitation.
Ekoru

Ekoru is a search engine focusing on the threat of climate change. They donate 60% of their monthly revenue to one of several partner charities ranging from reforestation to climate action. With this, they aim at selecting a different charitable cause every month.
They are also more of a privacy search engine by standing for civil rights by not storing any user or search-related data on their servers. They also use renewable energy sources for its data centers.
What is the Difference Between a Web Browser and Search Engines?
A search engine is a way for individuals to search for content and have a list of website results appear for them. It’s a way for them to find web pages from other websites.
A web browser on the other hand is a piece of software or program that gets and displays web pages. Examples of search engines include Google, Bing, and Yahoo. Examples of web browsers include Firefox, Internet Explorer, and Google Chrome.
What are the Commonly Used Web Browsers?
After all those different kinds of search engines, you may be asking yourself about the difference between a search engine and a web browser. A search engine is what you use to search online.
But a web browser is merely the tool that allows you to perform the search. These occasionally get confused because Browsers like Chrome or Firefox have a search bar that takes you to your Google, Bing, or other search results. But those search bars are powered by the search engine extension.
Consider the web browser as the vehicle. Search engines are the driver behind the wheel taking you to your desired destination based on what you search. But you still need a vehicle to get you there.
Common web browsers include Google Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Internet Explorer, and more. We’ll get into some of the main features of popular web browsers below:
Google Chrome

Google’s Chrome browser is one of the most popular browsers out there today, and frankly to ever exist. It has thousands, if not millions of plugins, extensions, and customizable features that allow you to make your browsing and search experience all your own. It’s a cross-platform web browser meaning you can use multiple search engines and tools within the browser.
If you log into your Google account while using Chrome, Google can track your movements across the web. It can lead to a more customized search experience, but at the same time cuts down on some privacy.
Google Chrome uses cookies to personalize ads, help you with near-me searches, and more. Though you can adjust privacy controls. Chrome allows you to customize your view and set which search engine you want to use to browse.
Chrome is extremely robust and has seemingly unlimited resources. It’s popular for a reason. It’s the default browser for many computer platforms and offers a free download if your computer doesn’t already come with it pre-installed.
Safari

Safari is Apple’s default web browser that comes on all iPhones, iPads, Macs, and any Apple device. Apple brands Safari as the world’s fastest browser. Though of course, that depends on your internet connection speed.
Safari can be really useful if you’re an Apple user with multiple devices. It can save passwords, preferences, bookmarks, history, and more across all your devices when you’re nearby. Safari has about 54% of the search engine market share for mobile browsing in the U.S.
Apple also likes to tout its privacy abilities. Safari will track some online movements, but maybe not as much as other platforms. It has privacy protections built in, including “Intelligent Tracking Prevention that identifies trackers and helps prevent them from profiling or following you across the web.” And it has a built–in privacy report so you can see what websites are tracking or profiling you based on your browsing habits.
They use Javascript to power their browsing capabilities. Safari also provides many customization options where you can create your own browsing experience based on your own preferences. You can set Google, Bing, or various search engines as your default search engine.
Brave

Brave is the latest web browser making waves in the tech community. Like many privacy search engines, such as DuckDuckGo and Startpage, Brave is branding itself as a safe and private browser that gets to where you want to go online quickly.
Brave is free to download, lets you use a variety of search engines, and remembers site authentication information if you ask it to, but eliminates ads and ad trackers. Brave downloads less content from a website, which allows it to load quickly and eliminates ad trackers. The company also promises that it does not store any user data.
Brave is just like most browsers. It’s easy to navigate and understand. But what sets it apart is its commitment to privacy over anything else.
Firefox

Firefox is one of the most popular web browsers out there. It’s also known as Mozilla Firefox, backed by a not-for-profit organization that doesn’t sell information to advertisers. It’s a free and open-source browser. It also is available to use as a mobile app for iOS and Android devices.
A lot of people have called Firefox slow, meaning it won’t get you to your desired website as quickly as Chrome. In 2017, Firefox heard these complaints and rebuilt the browser engine. Today it’s comparable to other browser speeds.
And similar to Brave, it uses ad-blocking technology to actually help a page load even faster. Firefox is very popular for those who still want easy functionality with more privacy than you would get on Chrome.
Opera

Opera is another good web browser available on just about any device. It’s been around for a while, with its first version released in 1995. Opera uses less processing capacity than other browsers with the same built-in ad–blocking technology that allows pages to load more quickly.
It has a free VPN that reduces online tracking. And it has cool technology that allows you to chat and browse at the same time with “built-in messengers on the edge of your browser” so you don’t have to keep switching between tabs and apps.
Internet Explorer

Internet Explorer (IE) has been around for a long time. And it gets a lot of flack for being slow and out of date. This is actually one of my favorite internet browser jokes even though it might be a bit inaccurate now.

Internet Explorer is no longer Microsoft’s default browser. That’s now Microsoft Edge (which I’ll talk about next). Microsoft first put IE into Windows 1995. By 2002, IE was the most used browser in the world.
It’s gone through a lot of different versions and will still get you online. Microsoft no longer fully supports it but instead defaults to Microsoft Edge.
Microsoft Edge

Microsoft Edge is the new default web browser installed on every new Windows computer. It replaces Internet Explorer. It has more features and runs more quickly than its predecessor, though it’s still trying to shake off the stigma. But it has enough features that it’s a legitimate competitor now.
Similar to Safari, when you sign in with a Microsoft account you can sync your bookmarks, history, passwords, and more across multiple devices. And you can add thousands/millions of extensions to it from the Microsoft Store, very similar to Google Chrome.
How Can I Tell Which Search Engine I’m Using?
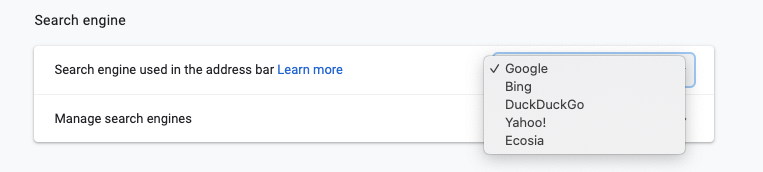
While every web browser is a little different, they all have similar features. You can set or find out your default search engine on every single web browser by accessing your browser’s settings.
For Chrome and Firefox, you have the option to go to Settings for your browser by going to the right–hand side and clicking on either three dots or three lines. When you go into settings, you can scroll down to “Default Search Engine”.
To easily find this without scrolling, just hit Control-F on a Windows computer, or Command-F on a Mac device and then type in “Search Engine”. It will help you locate it on the page.

How Do I Optimize My Website for Different Types of Search Engines?
We’ve gone through a lot of information in this article. And since we’re an SEO company, which helps your website be optimized for different types of search engines, it’s hard to know what is right or what to do with so many different kinds of search engines.
However, Google is the world standard. Google makes moves in the search community and most other platforms follow. So Google is emphasizing a good user experience and accurate content. So do all the other search engines.
At Boostability, we optimize websites with Google’s algorithm in mind. Because what is good for Google optimization will often be reflected across all search engine platforms. Google sets the standard, and other platforms follow.
And what is good for SEO on one platform, is good for them all. Optimizing your site will never hurt, no matter where your customers search!
Ready to get started with SEO to show up across all these platforms? We can help you! Boostability offers white label SEO services around the world and we are ready to help you and your customers! Contact us today to get started.